shiitake mushroom
Shiitake Mushroom: A Rich History Rooted in Japanese Culture

Tokyo Terry
Posted on August 31, 2023
Share:
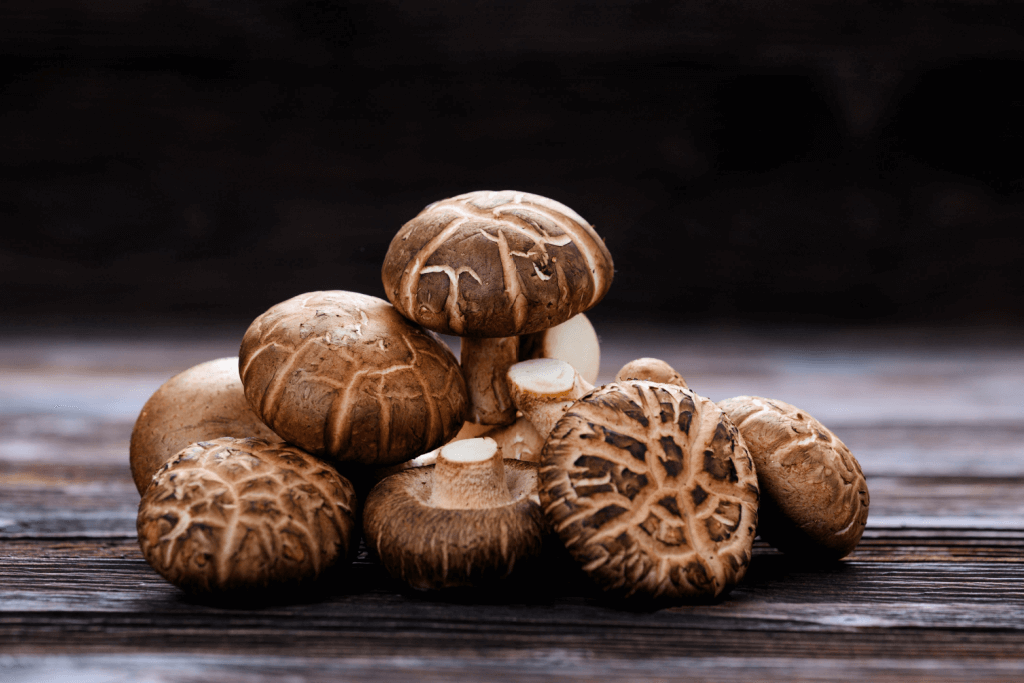

The rest of the world has adopted the methods used to cultivate the shiitake mushroom in Japan for centuries. These mushrooms (Lentinula edodes)are the most popular edible mushrooms globally. Techniques used in Japan to cultivate it have remained essentially unchanged for centuries. This nutritious mushroom is known worldwide for its health benefits and continues to reveal new uses.
Where did the shiitake mushroom come from?
The shiitake mushroom is native to East Asia. In the forests of Japan, it grows naturally on the rotting wood of hardwood trees such as chestnut, maple, and sawtooth oak. It also grows readily on Japanese tsuburajii, a species of Castanopsis tree native to Japan from which the fungus gets its name; the word shiitake is a combination of the Japanese kanji for tsuburajii(椎) and take (mushroom)(茸).

The shiitake mushroom does not grow directly on the ground and is only the “fruit” of the Lentinula fungus. The main body of shiitake, the stringy mycelium, grows in the soil. When trees die, the mycelium enters them from the ground, and shiitake mushrooms grow on the rotting wood. The mushroom only begins growing when the temperature, moisture, and surrounding nutrients are perfect.
Warm-weather shiitake strains appear in the summer and beginning of fall, while cold-weather types fruit in early spring and late fall. Some shiitake strains produce mushrooms over a broader range of temperatures, which spread and produce mushrooms more quickly.
How do people grow shiitake mushrooms?
People gathered wild shiitake mushrooms from decaying forest trees before they started farming them. Harvesting the mushrooms led to more in the same area all year round, resulting in shiitake becoming a highly convenient food source requiring minimal care.
Traditional Shiitake Mushroom Cultivation
Over time, people discovered that placing cut tsuburajii logs in areas where shiitake mushrooms grew caused the mushrooms to also grow on the logs. This spawned the cultivation of wild shiitake in the forests of Japan during the Nara period. People call these wild-grown mushrooms yama shiitake.

Unfortunately, overharvesting caused wild shiitake to become less abundant in Japan’s forests. A new cultivation method was necessary to meet the high demand for this delicious mushroom. Most people use two methods for large-scale shiitake cultivation. Both methods originated in Japan and have since been adopted by mushroom farmers across the globe. Though similar in approach, the two techniques produce noticeably different results. And there are advantages and disadvantages to each.
The Log Method
In 1796, a Japanese horticulturist, Sato Churyo, created the first Japanese guide on cultivating shiitake mushrooms, establishing standardized techniques. Later on, in 1914, Dr. Shozaburo Minura, a mycologist (a person who studies fungi), devised a method for growing shiitake on logs, innovating mushroom cultivation away from the forest setting.
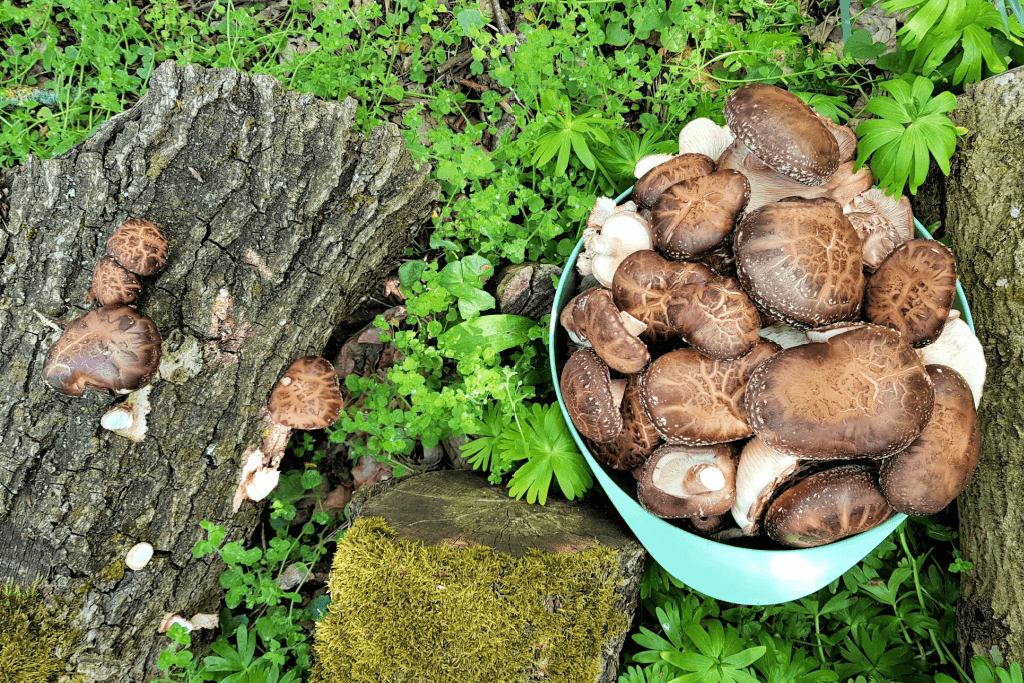
The method was so successful that shiitake production moved out of the forests and onto farms. It marked the beginning of large-scale production, and many Japanese shiitake farmers still use this method today. This method is very similar to the traditional method of freshly cut logs. However, the farmers add the mushrooms directly to the log for this method.
If stored outside, the growing shiitake is at greater risk of being damaged by weather and pests or eaten by animals. The mushrooms must first break down the fresh hardwood of the logs to obtain nutrients, which takes time. It can take more than two years for the mushrooms to begin growing. And when they emerge, they usually only do so twice a year. This limits the supply of mushrooms outside of the harvest seasons unless they are dried for storage.
Are you interested in enjoying traditional food that might feature shiitake mushrooms? Check out Sakuraco! Sakuraco sends traditional Japanese sweets, snacks, and tableware from across Japan to your door so that you can enjoy the experience!
The Sawdust Method
This method was developed to increase the number of annual harvests so that fresh mushrooms are available all year round. Most of the shiitake grown in Japan uses this technique. As the name suggests, sawdust is used instead of logs. First, nutrients are mixed with the sawdust. The smaller pieces of wood allow the mycelium to access the nutrients more efficiently. Next, shiitake mycelium is added, and the mixture is placed into bags or containers. This makes indoor storage much more convenient and easier to control the growing conditions.
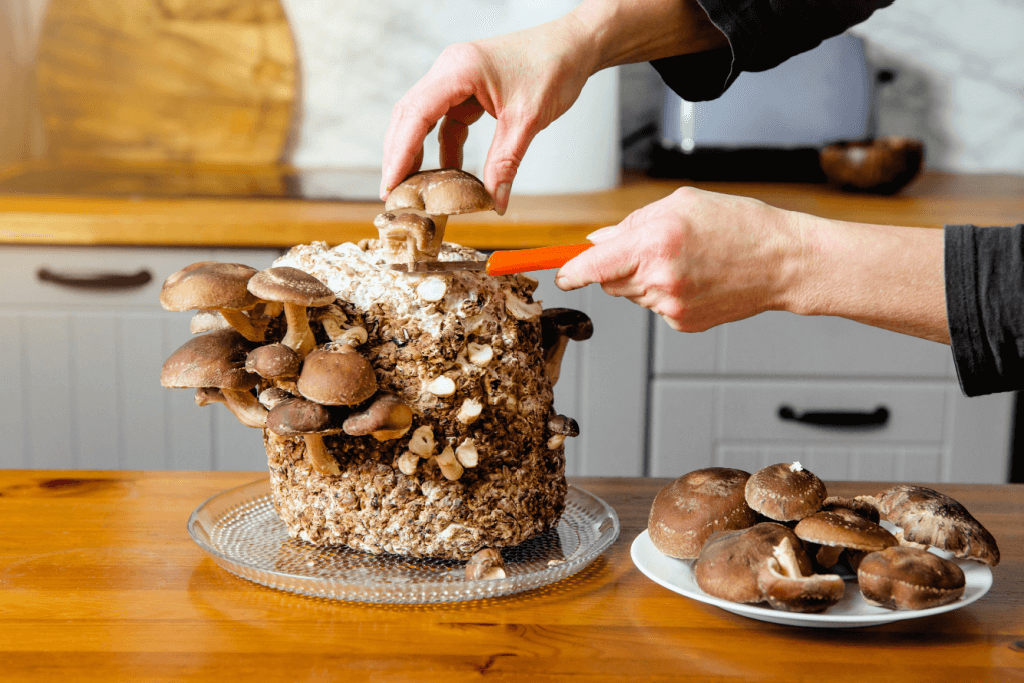

The efficiency of the sawdust method results in shorter mushroom growing cycles, so mushrooms are available for harvest in about six months. Shiitake production is consistent and frequent, so fresh mushrooms can be available throughout the year. In addition, the perfectly controlled conditions result in more shiitake. As a result, the flavor and aroma of shiitake grown using this method may be less intense. Fortunately, when eaten, these mushrooms are less dense and have a lighter, fluffier consistency.
Shiitake Mushroom Quality
After harvesting, shiitake mushrooms receive grades ranging from AA (highest quality) to C (lowest ranking). Grading considers size, flavor, aroma, and overall quality. Appearance and grade depend on production method, growth stage, and harvest time.
Donko Shiitake
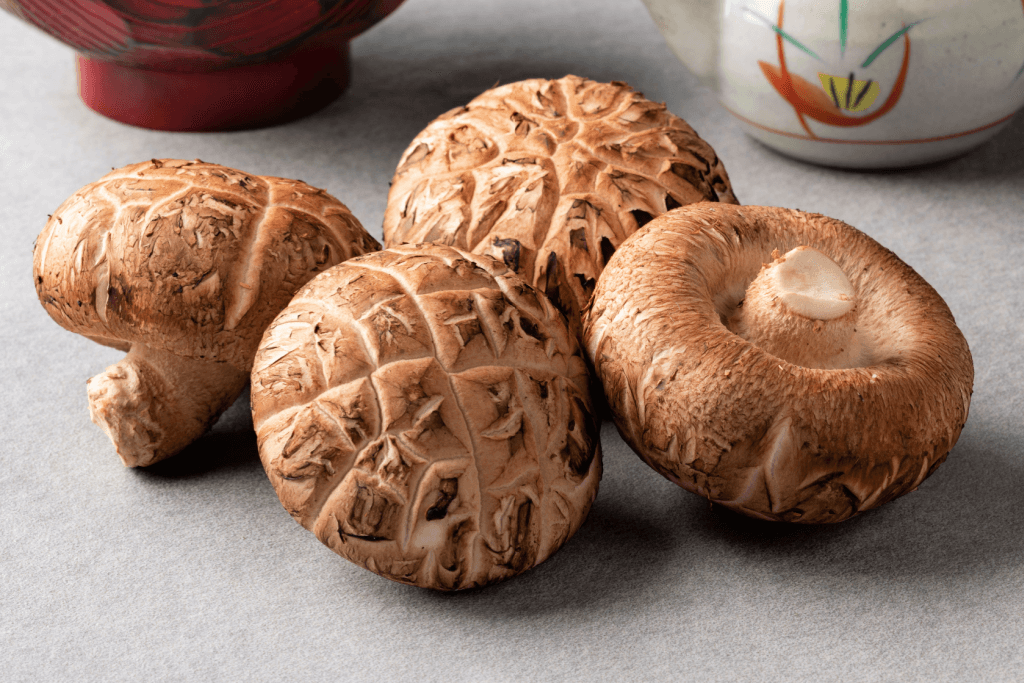

These are high-quality shiitake that farmers harvest in winter or spring. Because they develop in the winter–when there’s less sunlight–donko shiitake have a thick texture with a savory umami flavor. Having developed slowly during the winter, they are denser in colder weather and less sunlight with a meat-like, umami flavor. Donko shiitake are ideal for cooking as they are served fresh and can withstand heat. The highest quality shiitake generally grew more slowly, resulting in thicker caps.
Koshin and Koko Shiitake
Also known as “summer” shiitake, this grade of mushroom experienced long periods of intense sunlight. As a result, they increase, achieve their full size, and develop large caps. Though their color and flavor are not as intense, their large caps allow for more “gills” on their undersides, which produce a more detectable aroma. They are prominent in dishes like sushi, where sliced shiitake maximizes flavor and smell.
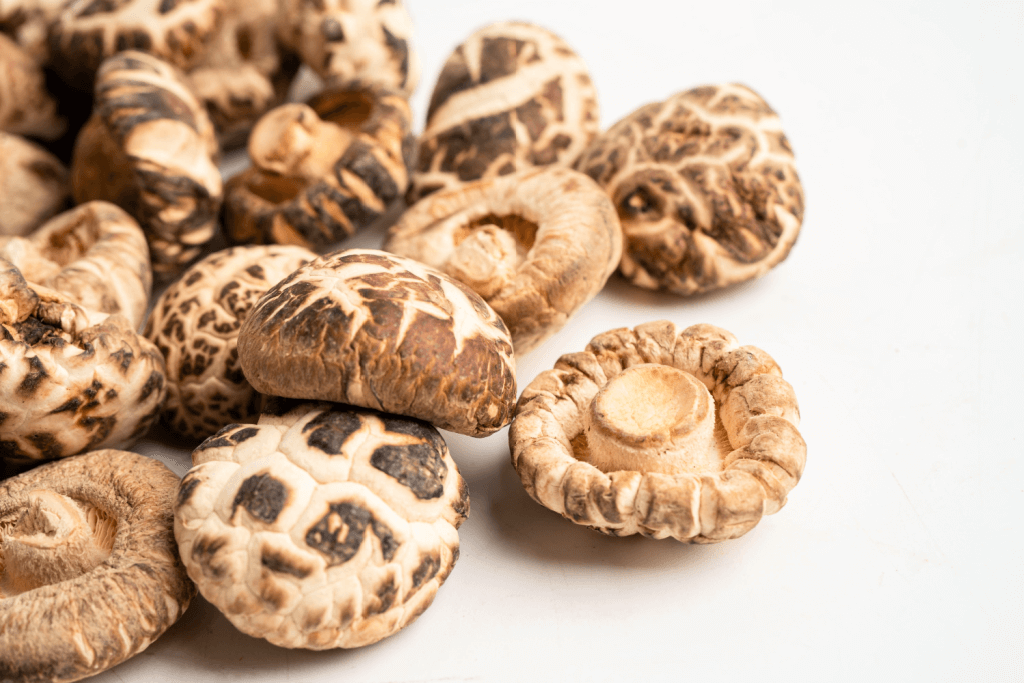

On the other hand, koko is a mid-grade shiitake with qualities between the donko and koshin. Mushrooms of this quality are best fresh and dried. Additionally, they’re suitable for barbecue dishes, stews, and soups because they retain their quality while boiling.
What are the health benefits of shiitake mushrooms?
Shiitake contains a unique combination of nutrients that have earned it a place on the list of healthiest foods. Vitamins A, B2, B12, C, and D are all present in the fungus and necessary trace elements such as calcium, copper, iron, selenium, zinc, and manganese. The mushroom is also packed with numerous enzymes, some improving digestion and lowering cholesterol.
Despite the benefits and being an ingredient in countless Japanese and East Asian shiitake mushroom recipes, consuming raw shiitake should be avoided. Although uncommon, raw or even undercooked shiitake can result in an allergic reaction known as shiitake dermatitis.
In conclusion, shiitake mushrooms are a staple in Japanese cooking and hold vital roles in worldwide medicinal and manufacturing sectors. Their significance and unique forest relationship underscore their sustainability. These versatile fungi bridge the gap between nature and human requirements, showcasing the harmonious interaction between the two. Have you ever tried cooking with shiitake mushrooms? We’d love to hear about your experiences and thoughts. Feel free to share in the comments below!

Discover authentic flavors with Sakuraco
Get Sakuraco 

Discover authentic flavors with Sakuraco
Get Sakuraco 
Related Articles

Yokohama Chinatown: Everything You Need to Know!
Yokohama, a city just south of Tokyo, is home to the largest of Japan’s three Chinatowns, called “chukagai” in Japanese. Established in the late 19th century, Yokohama Chinatown is a historic area home to hundreds of businesses.

Yamato Period: A Look at Japan’s Early Path to Unity
The Yamato Period laid the foundation for modern Japan. Powerful clans emerged to shape the islands’ future and form the country’s first early states.

Kyoto Shrines: Five Best Ones to Visit!
Kyoto shrines preserve history within their walls, and their network carries the old days into modern Japan. Visiting them can be a memorable way to learn about Japan’s past and understand how spiritual traditions coexist with modern life.

Cherry Blossom Flower Variety Across in Japan: The Ultimate Guide!
Many people know the soft pink cherry blossoms. However, sakura in Japan includes a wide variety.



