lotus root
Lotus Root: Everything You Need to Know!
Thuy Fang
Posted on January 26, 2024
Share:
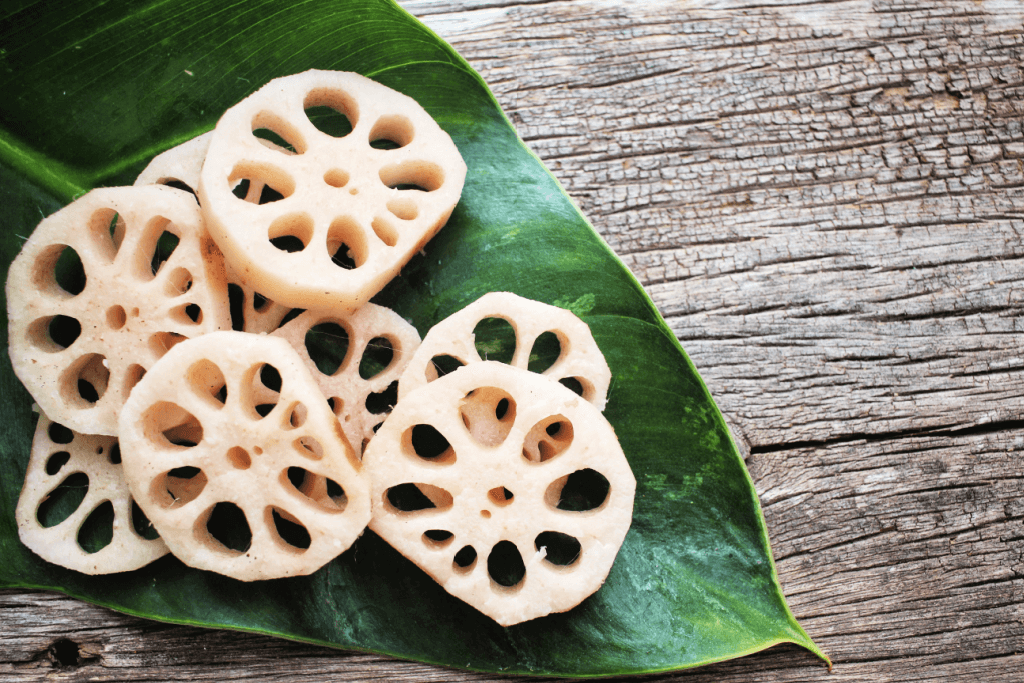

Lotus root, a star in Japanese cooking, is tasty and super healthy. For Japanese people, this gift from nature is more than just a veggie; it’s a cultural symbol representing good things in the future. Come with us to explore the wonders of this edible rhizome!
What is lotus root?
Lotus root, also called renkon in Japanese, comes from a beautiful flower with a special meaning in Buddhism. It’s a versatile and ancient ingredient used a lot in Asian cuisine. Lotus plants are found in Asia, Australia, New Guinea, and some parts of the Middle East. They grow in muddy water, and people collect their roots from August to fall.
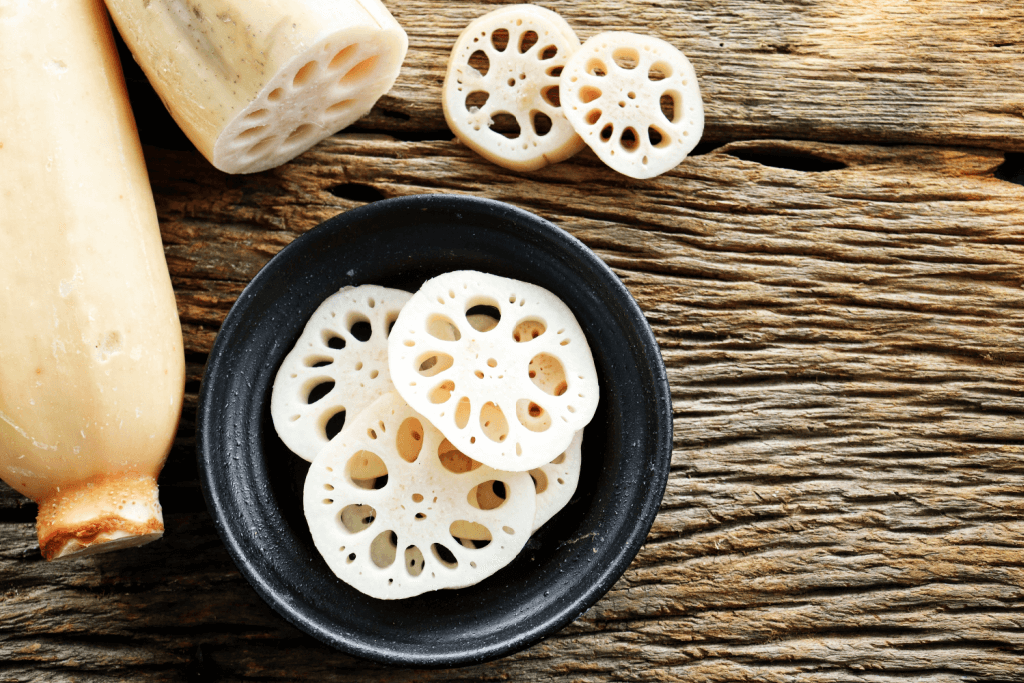

According to records of Joriku Fudoki, people in Japan have been eating the root for a very long time. These records mention that people in Ibaraki Prefecture already enjoyed this incredible starchy vegetable. A lord in Kumamoto started eating it in the 17th century because it was said to be good for health. During the Meiji period, renkon became even more popular when a type of lotus from China came to Japan.
When you slice the long brown roots, they reveal an intricate lace pattern with tiny holes, giving them a unique appearance. It has a crunchy texture with a bit of sweetness and tanginess, similar to water chestnuts. It’s a common ingredient in Japanese and Southeast Asian cooking, used in salads, stir-fries, steamed dishes, soups, and even tempura.
What are the health benefits of lotus root?
Beyond its culinary uses, this tuber has been integral in traditional medicine. Its health benefits stem from its rich nutrient profile. Moreover, it also has fiber that helps your tummy work well and keeps your cholesterol down. It also has complex carbohydrates that release energy slowly, helping control blood sugar.
Plus, it gives you essential vitamins like B2, B6, and C to support immune function and collagen synthesis. In addition, it can also provide you with many helpful minerals like potassium for blood pressure regulation and phosphorus for DNA creation and cell repair. All these things together keep your body healthy and strong.
Besides its possible protection for the liver and stomach, renkon can also help reduce inflammation, prevent diabetes, and keep your gut healthy. Furthermore, with its crunchy texture and many health advantages, such as reducing stress and being gluten-free, adding lotus tuber to your diet is an innovative and tasty option.
Are you looking for delicious snacks featuring ingredients like lotus root? Check out Sakuraco! Sakuraco delivers traditional Japanese snacks, teas, sweets, and snacks from local Japanese makers directly to your door so you can enjoy the latest treats directly from Japan!
Which dishes use renkon?
Kinpira renkon
Kinpira renkon is made by cooking thin slices of lotus tuber exceptionally. First, they’re stir-fried, then simmered in a tasty sauce with soy sauce and mirin. Sometimes, people in Japan add a bit of spicy chili peppers for a kick. The name of this food also comes from the way it’s cooked.
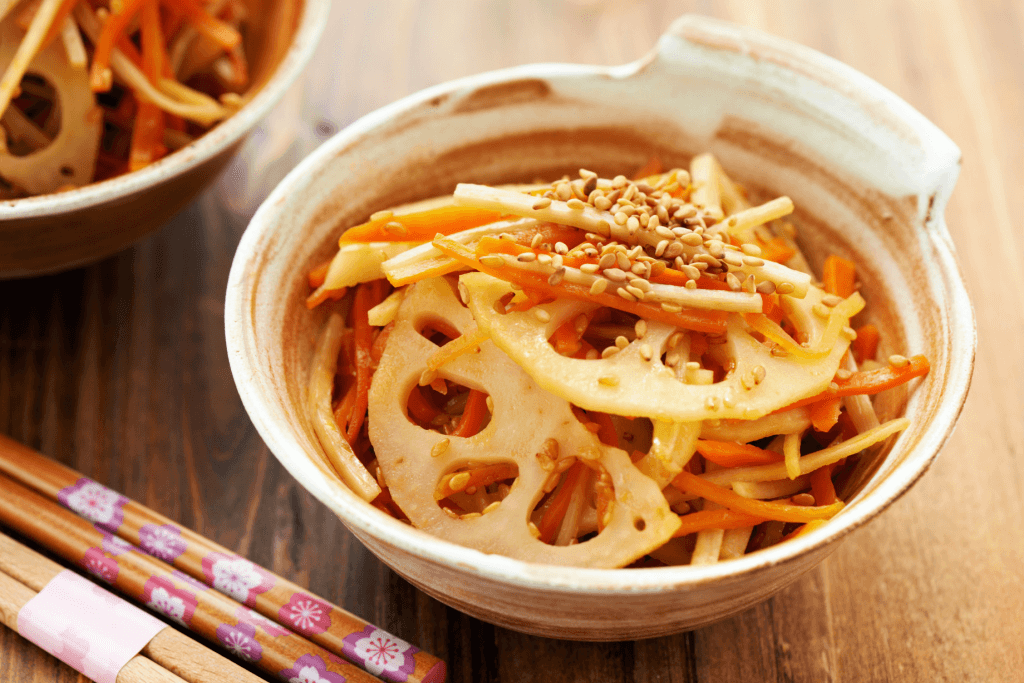

This dish is a classic in Japan, where they often use the same cooking method for other vegetables like carrots and burdock root. It’s simple but delicious, with a crispy and tender mix of flavors. Whether you try it at a Japanese restaurant or make it at home, kinpira renkon may be a tasty treat for your lunch!
Renkon chips
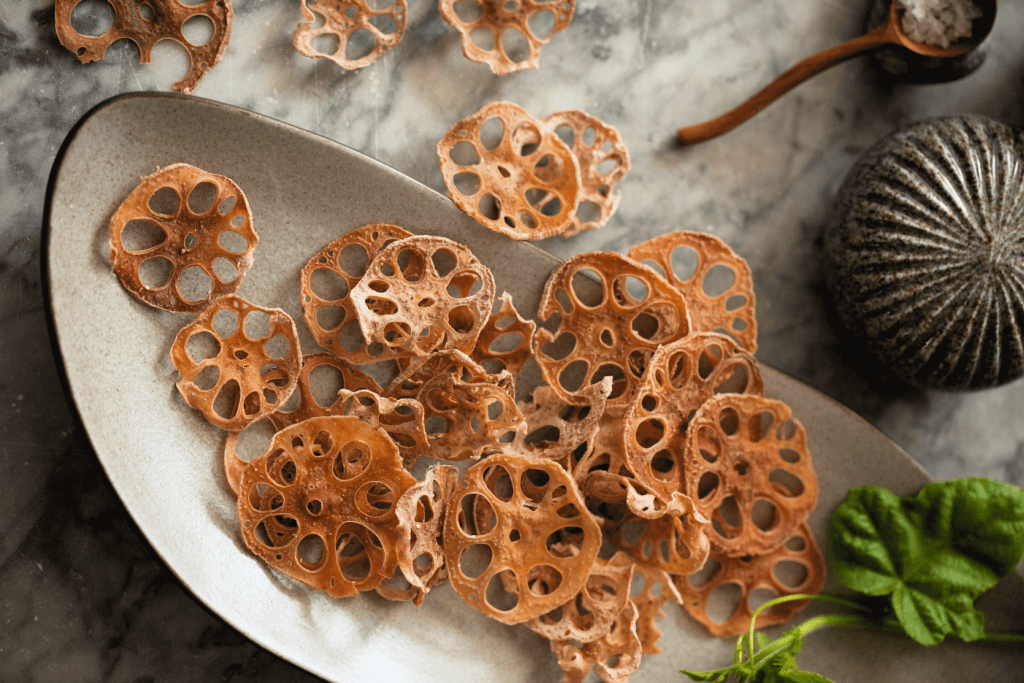

These chips are a tasty treat and a healthier alternative to traditional potato chips. They’re sweet and super crunchy. Unlike their snack counterparts, these chips contain less oil and higher fiber content, making them a guilt-free snack option. To make renkon chips, we peel and slice the root, add some salt, and bake or fry until they’re crispy. These crunchy delights offer a unique and appealing shape and serve as excellent salad toppings.
Pickle lotus root salad (Su Renkon)
In this delicious dish, thin slices of lotus roots immerse themselves in a blend of mirin, rice vinegar, sugar, and salt to provide a delightful sweet and sour flavor. The outcome is a tasty and refreshing flavor that helps balance flavorful meals.
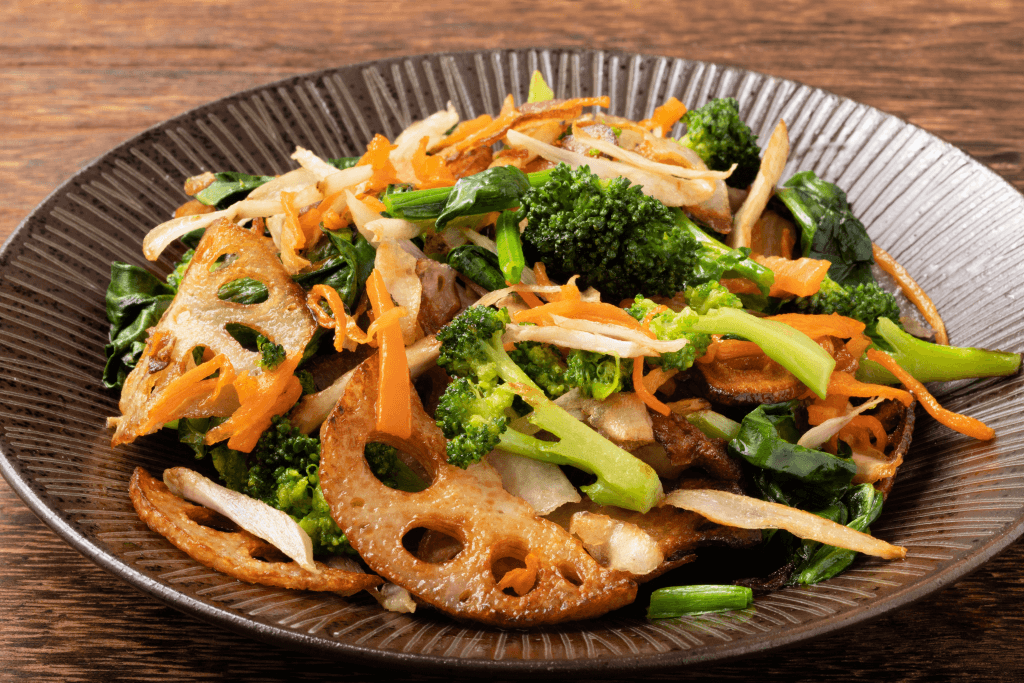

Su renkon is enjoyed throughout the year but holds a special place during the Japanese New Year festivities. This edible rhizome is seen as a lucky food during special times because its many holes represent a clear future view. People eat it to wish for good things and successes to happen to their families.
Why should I try lotus root?
In short, lotus root offers a flavorful experience and an exploration of a nutritious lifestyle. With its crunchy texture and unique flavor, renkon will surely add a special touch to your daily meals. Have you ever tried this interesting vegetable before? Share your thoughts in the comments!

Discover authentic flavors with Sakuraco
Get Sakuraco 

Discover authentic flavors with Sakuraco
Get Sakuraco 
Related Articles

Shinshu Apples: The Pride of Nagano’s Orchards
Right after Aomori, Nagano consistently ranks among Japan’s top apple producers. But its fame doesn’t stop there! Shinshu apples are renowned worldwide, cherished both as fresh fruit and in a variety of delicious apple-based treats. That’s more than enough reason for us to dive in and discover what makes them so special!
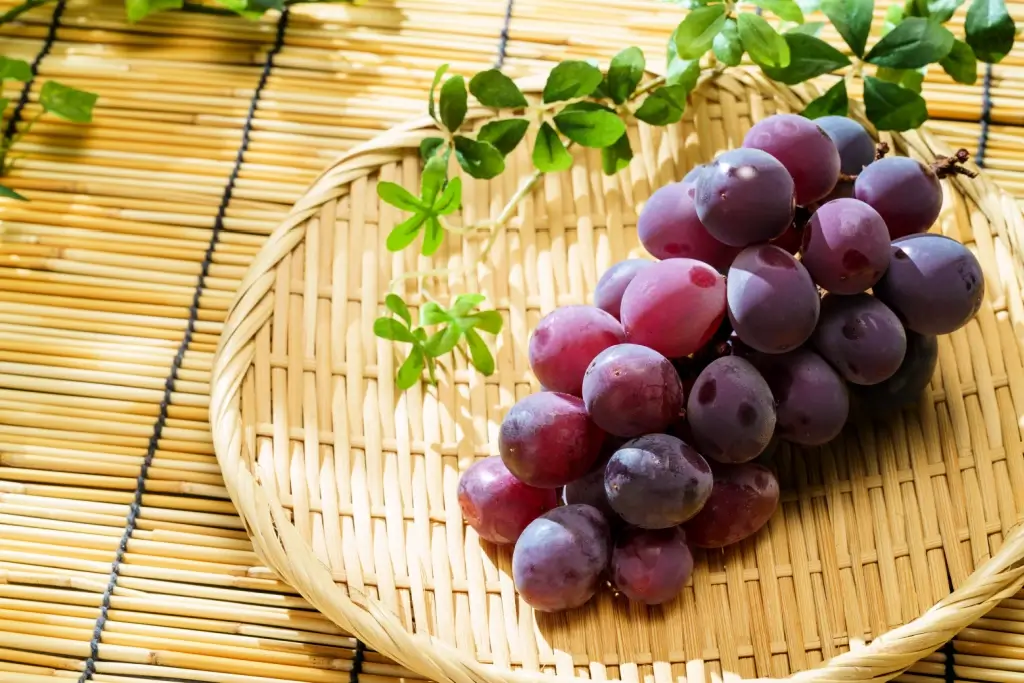

Kyoho Grapes: A Jewel of Japanese Vineyards
From late summer to early fall, you can easily spot stunning Kyoho grapes elegantly packed in gift baskets at supermarkets and specialty fruit shops across Japan. These treasured fruits are frequently presented as elegant gifts, representing both excellence and thoughtful friendship.
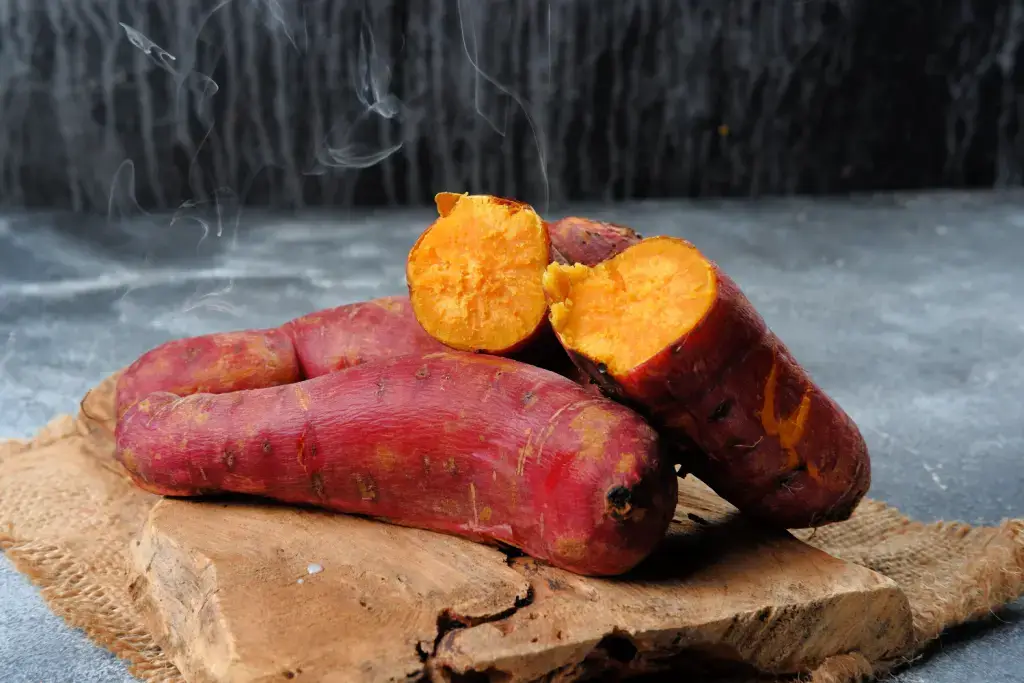

Japanese Sweet Potato Delights: Ultimate Guide of Wagashi To Look Out For!
The Japanese sweet potato, or satsumaimo, is a root vegetable characterized by its vibrant purple skin and naturally sweet, golden-yellow flesh.
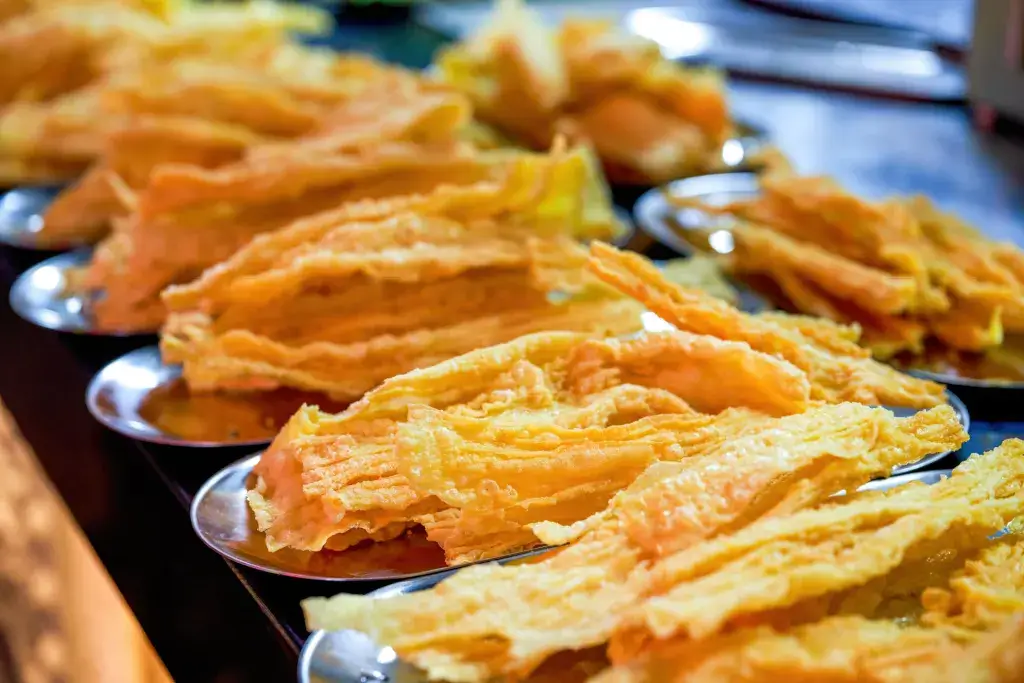

Tofu Chips: What is the Story Behind Yuba?
Tofu is a staple of Japanese cuisine and is consumed in many forms. It is commonly seen in its soft, jelly-like state at supermarkets across Japan. But did you know that it can also be transformed into a crunchy snack and eaten in the form of chips? Their unique texture has been known since the 10th century.



